On this page:
Latest information about where, when and why environmental water may be delivered to the Yarra system and the environmental objectives being targeted is available in this year’s seasonal watering plan.
The seasonal watering plan also contains information about how environmental flows could support cultural, social, recreational and economic values in the Yarra system.
Watering data for the Yarra system and the wider central region is updated quarterly. Visit current watering releases to find out more.
To find out the current environmental water entitlements held by the VEWH in the Yarra system visit our water holdings.
Information about the ownership of water entitlements in the Yarra system can be found under the Entitlements and Compliance section of the Yarra basin page at Victorian Water Accounts.
Waterway manager
Storage manager
Environmental Water Holder
Victorian Environmental Water Holder
Traditional Owners
Bunurong Land Council Aboriginal Corporation - statutory authority for the management of Aboriginal heritage values and culture, under the Victorian Aboriginal Heritage Act 2006.
Wurundjeri Woi-Wurrung Cultural Heritage Aboriginal Corporation - statutory authority for the management of Aboriginal heritage values and culture, under the Victorian Aboriginal Heritage Act 2006.
System overview
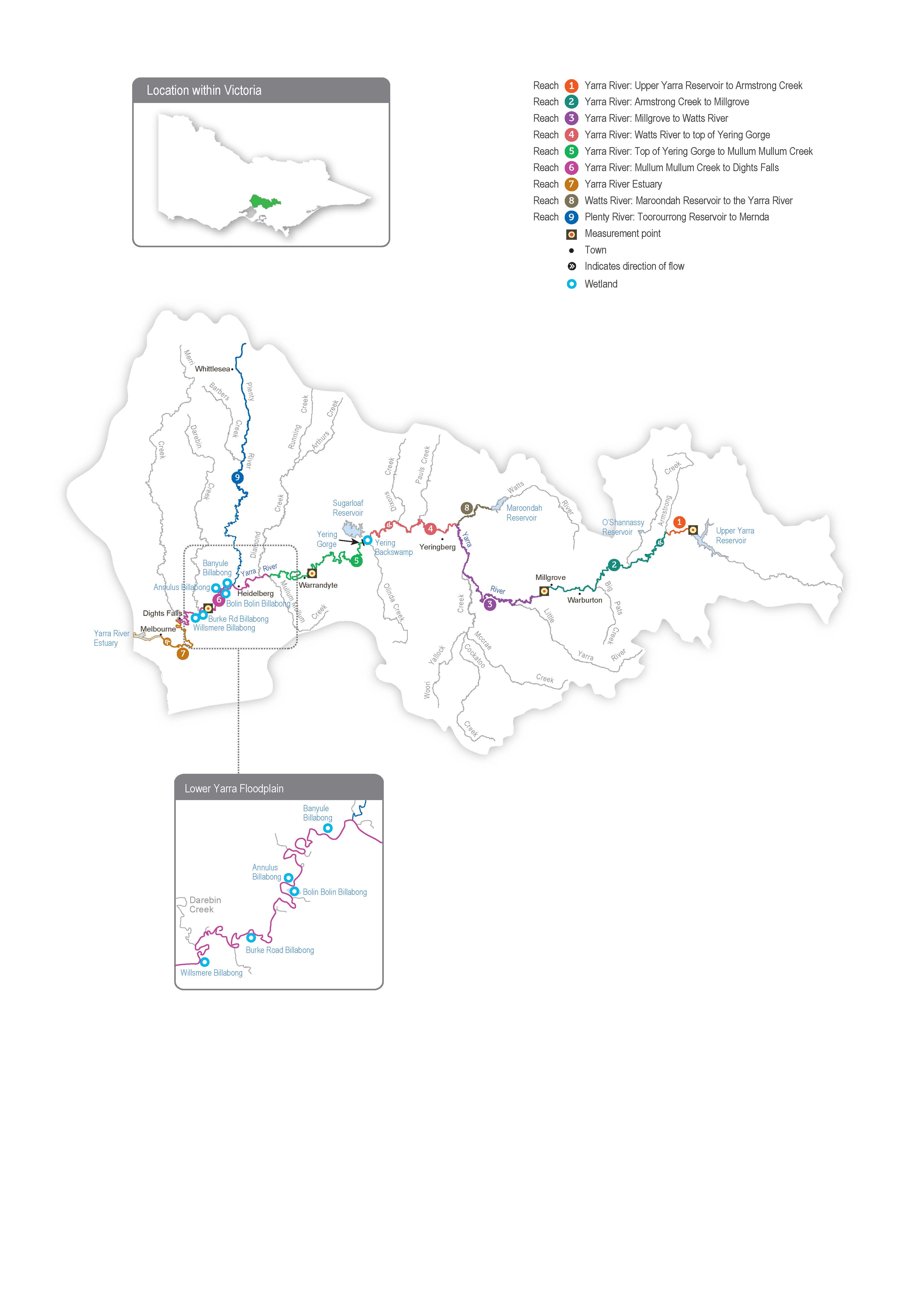
The Yarra system includes Birrarung (Yarra River), the Plenty River and Yarra Billabongs.
Birrarung (Yarra River) flows west from the Yarra Ranges above Warburton through the Yarra Valley and then opens out into a wider plain as it meanders through the suburbs and city of Melbourne before entering Port Phillip Bay. Over time, the Yarra River below Warrandyte has been straightened, widened and cleared of fallen trees and other natural habitat features as Melbourne has developed.
Up to 400,000 ML per year (long-term average diversion limit) can be harvested from the Yarra system for consumptive use in Melbourne and surrounding areas. The Upper Yarra, O’Shannassy and Maroondah reservoirs harvest water from headwater tributaries, and a pump station at Yering Gorge is used to harvest water from the Yarra River to Sugarloaf Reservoir.
Tributaries, including Armstrong Creek, McMahons Creek, Starvation Creek, Woori Yallock Creek and the Watts and Little Yarra rivers, influence the flow in the upper reaches of the Yarra River. Urbanised tributaries (such as Olinda Creek, Mullum Mullum Creek, Diamond Creek, Plenty River and Merri Creek) provide additional water to the middle and lower reaches of the Yarra River.
Water for the environment can be released from the Upper Yarra, Maroondah and O’Shannassy reservoirs to support environmental processes and outcomes in downstream river reaches and wetlands. Requests can also be made to cease harvest from the Yarra River at the Yering Gorge Pumping Station, allowing the flow to pass down the whole river system. The priority Yarra River reaches for environmental watering are 2 and 5. Reach 6 is also a priority in summer and autumn to manage poor water quality upstream of Dights Falls, as flow targets in reach 5 may not be sufficient. Water for the environment delivered to reaches 2 and 5 will help meet flow targets in other reaches. Occasionally, watering actions met naturally in reaches 2 and beyond are not achieved in reach 1 due to the lack of unregulated tributary inflows immediately downstream of Upper Yarra Reservoir. In those cases, water for the environment can be used to meet flow targets in reach 1.
The Plenty River rises from the slopes of Mount Disappointment in the Great Dividing Range about 50 km north of Melbourne. It flows downstream through rural and semi-rural areas and Plenty Gorge before joining the Yarra River near Viewbank, east of Banyule Flats Reserve. Yan Yean Reservoir is located off the waterway north of Plenty Gorge, and it receives a flow from Toorourrong Reservoir via a channel. The Plenty River has not received managed environmental flows before, but there may be opportunities to deliver water for the environment from Yan Yean Reservoir in the coming years.
Environmental values
The upper reaches of the Yarra River (reaches 1-3) have good-quality streamside and aquatic vegetation and provide habitat for native fish species, including river blackfish, mountain galaxias and common galaxias. The middle and lower reaches of the Yarra River (reaches 4-6) flow through forested gorges, cleared floodplains and some highly urbanised areas, and they support the native fish population, including Australian grayling, river blackfish, Macquarie perch and tupong. Macquarie perch were introduced to the Yarra River last century, and its population is now considered one of Victoria’s largest and most important.
The Plenty River (reach 9) provides habitat for waterbugs and native fish species (such as common galaxias). Platypus have been detected in the Plenty River in the past, but none were recorded in recent surveys.
Billabongs are an important feature of the lower Yarra River floodplain between Heidelberg and Dights Falls and further upstream near Yarra Glen and Woori Yallock. The billabongs support distinct vegetation communities and provide foraging and breeding habitat for waterbirds and frogs. Except in times of high flow, most billabongs are disconnected from the Yarra River.
Page last updated: 01/05/25